History of Banking in India PDF: Check Their Origin, Evolution, Structure, and Roles
Jun 30 2025
The history of banking in India reflects the evolution of the country’s financial system, from ancient money lending practices to the establishment of modern banking institutions. The Indian banking sector has played a pivotal role in supporting economic development, facilitating trade, and promoting financial inclusion.
The journey of Indian banking began with traditional indigenous bankers and evolved through the founding of key institutions such as the Bank of Hindustan (1770), the Presidency Banks, and later the formation of the Imperial Bank of India in 1921, which eventually became the State Bank of India in 1955. Major milestones such as the nationalization of banks in 1969 and 1980, the establishment of Regional Rural Banks (RRBs), NABARD, and the liberalization of the banking sector in the 1990s shaped the modern banking landscape of India.
For aspirants preparing for Banking, SSC, UPSC, and other government examinations, understanding the history of banking in India is crucial for answering questions in the General Awareness, Banking Awareness, and Economy sections. This article provides a timeline of key events, major reforms, and institutions that have defined India’s banking sector.
History of Banking in India PDF Download Links
Click the links below to download the History of Banking in India 2025. Candidates can make use of these PDFs for their upcoming bank exam preparation.
History Of Banking In India PDF Before Independence
History Of Banking In India PDF - After Nationalisation
History Of Banking In India PDF - Private Banks
History of Banking in India
1. Before Independence (1770 to 1947)
There were quite a few banks established during this time.
-
The history of Banking in India began with the establishment of the Bank of Hindustan in 1770, but it stopped operating by 1832.
-
During this period, over 600 banks were established. However, very few were able to succeed.
-
During the British rule in India, the East India Company established three banks and called them the Presidential Banks, i.e.,
-
Bank of Bengal
-
Bank of Bombay
-
Bank of Madras
-
These three banks were later merged into one single bank in 1921, which was called the “Imperial Bank of India.”
-
The Imperial Bank of India was later nationalized in 1955 and named The State Bank of India, the largest Public sector Bank.
-
Given below is a list of other banks that were established during the pre-Independence period, along with the history of banking in India.
History of Banking in India Before Independence |
|
Bank Name |
Year of Establishment |
|
Allahabad Bank |
1865 |
|
Punjab National Bank |
1894 |
|
Bank of India |
1906 |
|
Central Bank of India |
1911 |
|
Canara Bank |
1906 |
|
Bank of Baroda |
1908 |
The reasons why many major banks failed to survive during the pre-independence period, the following conclusions can be drawn:
-
Indian account holders had become fraud-prone.
-
Lack of machines and technology.
-
Human errors & are time-consuming.
-
Fewer facilities.
-
Lack of proper management skills.
First Bank of India
The "Bank of Hindustan," which was founded in 1770 and had its headquarters in Calcutta, the then-capital of India, was the country's first bank. The agent of the Alexander and Company house established the first bank of India. It is currently nonexistent.
2. After Independence (1947 to 1991)
Following the history of banking in India before independence, which has observed some major changes in the banking industry scenario, and has developed a lot.
- Government, after Indian Independence, decided to nationalize the Banks because all the major banks were privately which was a cause of concern as people in the rural areas still turned to moneylenders for assistance.
Nationalisation of Banks in India
In the history of banking in India, the nationalization of banks is one of the important processes done by the Reserve Bank of India in the year 1949.
About Regional Rural Banks in India
|
Nationalisation of Banks in India |
|
|
Nationalization of Banks in India List |
Nationalization Year |
|
Allahabad Bank |
1969 |
|
Bank of India |
|
|
Bank of Baroda |
|
|
Central Bank of India |
|
|
Bank of Maharashtra |
|
|
Canara Bank |
|
|
Dena Bank |
|
|
Indian Overseas Bank |
|
|
Indian Bank |
|
|
Punjab National Bank |
|
|
Syndicate Bank |
|
|
Union Bank of India |
|
|
United Bank of India |
|
|
UCO Bank |
|
|
Andhra Bank |
1980 |
|
Corporation Bank |
|
|
New Bank of India |
|
|
Oriental Bank of Commerce |
|
|
Punjab & Sind Bank |
|
|
Vijaya Bank |
|
|
State Bank of Patiala |
1959 |
|
State Bank of Hyderabad |
|
|
State Bank of Bikaner & Jaipur |
|
|
State Bank of Mysore |
|
|
State Bank of Travancore |
|
|
State Bank of Saurashtra |
|
All these banks were later merged with the State Bank of India in 2017, except for the State Bank of Saurashtra, which was merged in 2008. The State Bank of Indore was merged in 2010.
Several reasons for nationalism in the banks of India are:
-
Nationalism led to an increase in funds and thereby improved the economic condition of the country.
-
It increased efficiency.
-
It helped in boosting the rural and agricultural sectors of the country.
-
This opened up a major employment opportunity for the people.
-
The profit gained by Banks was used by the Government for the betterment of the people.
-
The competition decreased, and work efficiency increased.
The post-independence phase was the one that led to the major development of the banking sector in India.
3. Liberalization Period (1991 to Till Date)
To provide stability and profitability to the Nationalised Public sector Banks, the Government decided to set up a committee under the leadership of Shri. M Narasimham to manage the various reforms in the Indian banking industry.
- The biggest development was the introduction of Private sector banks in India. RBI gave licenses to 10 Private sector banks to establish themselves in the country. These banks included:
-
Global Trust Bank
-
ICICI Bank
-
HDFC Bank
-
Axis Bank
-
Bank of Punjab
-
IndusInd Bank
-
Centurion Bank
-
IDBI Bank
-
Times Bank
-
Development Credit Bank
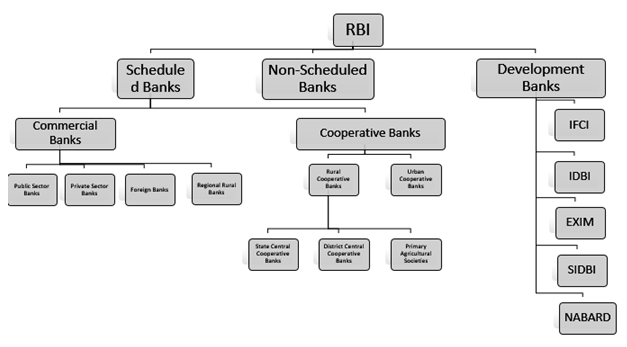
Indian Banking Structure
The current Indian banking structure has evolved over several decades in the history of banking in India.
-
Indian banking is set up to meet the country's economic demands for credit and financial services.
-
Every candidate for a position in banking and finance has to have a thorough awareness of the nation's current financial system, both for practical knowledge and test preparation.
-
The strength and effectiveness of the Indian banking structure increased dramatically after the financial sector reforms of 1991.
-
When compared favorably to the majority of developed nations, India's commercial banking industry is financially strong.
Banking System in India and Its Role
The banking system in India is considered the backbone of the nation's economy.
-
The main functions of the commercial banking system include borrowing to lending.
-
Receiving deposits and advancing loans are the two main functions of all commercial banks.
-
Other than these, there are five other functions of commercial banks, and they are the acceptance of deposits.
-
Banks mainly depend on the funds deposited with them by the public.
-
Advancing loans is another function.
-
Banks give loans to businessmen and firms, usually for short periods only.
-
Discounting bills of exchange or undies is another important function.
-
Banks transfer money from one place to another for their customers.
-
The final properties of the banking system provide miscellaneous functions, which include providing a locker, purchasing and selling of stocks, etc.
Components of the Banking System in India
The banking system is made up of the following sectors in India. The components of the banking system are given below.
Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is the central bank of India. The RBI was originally set up as a private entity in 1935, but it was nationalized in 1949.
-
The main purpose of the RBI is to conduct consolidated supervision of the financial sector in India, which is made up of commercial banks, financial institutions, and non-banking finance firms.
-
The RBI formulates, implements, and monitors India’s monetary policy.
-
The bank’s management objective is to maintain price stability and ensure that credit is flowing to productive economic sectors.
-
The RBI also manages all foreign exchange under the Foreign Exchange Management Act of 1999.
Scheduled Banks
Scheduled banks are those banks that are listed under Schedule II of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
-
The bank's paid-up capital and raised funds must be at least Rs. 5 lakh to qualify as a scheduled bank.
-
These banks are liable for low-interest loans from the RBI.
-
They also have membership in clearinghouses.
-
They also have numerous obligations to fulfill, such as maintaining an average daily Cash Reserve Ratio with the central bank.
Unscheduled Banks
Non-scheduled banks, by definition, are those that do not adhere to the RBI’s regulations.
-
They are not mentioned in the Second Schedule of the RBI Act, 1934, and are therefore deemed incapable of serving and protecting depositors’ interests.
-
Non-scheduled banks must also meet the cash reserve requirement, not with reserve banks, but with themselves.
-
They are generally smaller in size and have a range of influence that is somewhat narrow. '
-
They are risky to do business with due to their financial limitations.
-
The reserve capital of these banks is less than 5 lakh rupees.
Commercial banks
The term commercial bank refers to a financial institution that accepts deposits, offers checking account services, makes various loans, and offers basic financial products like certificates of deposit (CDs) and savings accounts to individuals and small businesses.
-
A commercial bank is where most people do their banking.
-
Commercial banks make money by providing and earning interest from loans such as mortgages, auto loans, business loans, and personal loans. Customer deposits provide banks with the capital to make these loans.
Public Sector Banks
A public bank is a financial institution in which a state, municipality, or public actors are the owners.
-
It is an enterprise under government control.
-
Public or 'state-owned' banks proliferated globally in the late 19th and early 20th centuries as vital agents of industrialization in capitalist and socialist countries alike; as late as 2012, state banks still owned and controlled up to 25 % of total global banking assets.
-
Proponents of public banking argue that policymakers can create public-sector banks to reduce the costs of government services and infrastructure; protect and aid local banks; offer banking services to people and entities underserved by private-sector banking, and promote particular kinds of economic development reflecting polities’ shared notions of social good.
-
A table of private-sector banks is given below.
List of Public Sector Banks in India |
|
Public Sector Bank |
Headquarters |
|
Punjab National Bank ( Merged with Oriental Bank Of Commerce and United Bank Of India) |
New Delhi |
|
Indian Bank( Merged with Allahabad Bank) |
Chennai |
|
State Bank of India |
Mumbai |
|
Canara Bank( Merged with Syndicate Bank) |
Bangalore |
|
Union Bank of India( Merged with Andhra Bank and Corporation Bank) |
Mumbai |
|
Indian Overseas Bank |
Chennai |
|
UCO Bank |
Kolkata |
|
Bank of Maharashtra |
Pune |
|
Punjab and Sind Bank |
New Delhi |
|
Bank of India |
Mumbai |
|
Central Bank of India |
Mumbai |
|
Bank of Baroda |
Gujarat |
Private sector Banks
In the history of banking in India, Private Sector Banks are those banks in which the majority of the stake is held by shareholders of the bank and not by the government.
-
RBL Bank, HDFC Bank, ICICI Bank, Yes Bank, etc. are the private sector banks in India.
-
They provide all the banking products and services to the customers.
-
These products include Fixed Deposits, Savings Deposits, RD, Home Loans, Personal Loans, Car Loan, Locker, Demat Facilities, Debit/ Credit Card, ATM, Foreign Exchange Transactions, Insurance, Wealth Management, Net Banking, etc.
-
Private banks are known for introducing information technology into the banking system.
List of Private Sector Banks |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
Name of the Bank |
Branches |
Establishment |
Headquarter |
|
Axis Bank |
4528 |
1993 |
Mumbai, Maharashtra |
|
Bandhan Bank |
670+ |
2015 |
Kolkata, West Bengal |
|
CSB Bank |
417 |
1920 |
Thrissur, Kerala |
|
City Union Bank |
700+ |
1904 |
Kumbakonam, Tamil Nadu |
|
DCB Bank |
334 |
1930 |
Mumbai, Maharashtra |
|
Dhanlaxmi Bank |
270+ |
1927 |
Thrissur City, Kerala |
|
Federal Bank |
1284 |
1931 |
Aluva, Kochi |
|
HDFC Bank |
5430 |
1994 |
Mumbai, Maharashtra |
|
ICICI Bank |
5288 |
1994 |
Mumbai, Maharashtra |
|
IDBI Bank |
1892 |
1964 |
Mumbai, Maharashtra |
|
IDFC FIRST Bank |
260 |
2015 |
Mumbai, Maharashtra |
|
IndusInd Bank |
2000 |
1994 |
Pune, Maharashtra |
|
J&K Bank |
1038 |
1938 |
Srinagar, Jammu, and Kashmir |
|
Karnataka Bank |
857 |
1924 |
Mangaluru, Karnataka |
|
Karur Vysya Bank |
779 |
1916 |
Karur, Tamil Nadu |
|
Kotak Mahindra Bank |
1500+ |
2003 |
Mumbai, Maharashtra |
|
Nainital Bank |
150 |
1922 |
Nainital, Uttarakhand |
|
RBL Bank |
398 |
1943 |
Mumbai, Maharashtra |
|
South Indian Bank |
876 |
1929 |
Thrissur, Kerala |
|
Tamilnad Mercantile Bank |
509 |
1921 |
Tuticorin, Tamil Nadu |
|
YES Bank |
1000+ |
2004 |
Mumbai, Maharashtra |
Foreign Banks
-
Foreign Banks in India have a vast history of banking in India do make a share of 7% in the total Indian Banking Sector, giving a profit of 11% to the Indian economy, and there is only a 1% branch network of Foreign Banks in India, as they are mostly niche players by focusing more on trade finance, wholesale lending, external commercial borrowing, treasury service, and investment banking.
-
These banks are under the regulation of the Reserve Bank of India, as RBI allows either the branch mode or wholly-owned subsidiary, and these Single Mode of Presence Banks are very less in India but manage their customers with good transactions, giving good capital as guided by RBI regulations.
There are 45 international/foreign banks in India.
Foreign Banks |
|
Foreign Sector Bank |
Bank Website |
|
AB Bank Limited |
abbl.com |
|
Abu Dhabi Commercial Bank Ltd. |
adcbindia.com |
|
American Express Banking Corp. (AEBC) |
americanexpress.com/india/homepage.shtml |
|
ANZ Banking Group Ltd. |
anz.com |
|
Bank of America N.A. |
bankofamerica.com |
|
Bank of Bahrain & Kuwait BSC |
bbkonline.com |
|
Barclays Bank Plc |
barcap.com |
|
BNP PARIBAS |
bnpparibas.com |
|
Citibank N.A. |
Citibank.co.in |
|
Cooperative Rabobank U.A |
rabobank.com/india |
|
Credit Agricole Corporate And Investment Bank |
ca-cib.com |
|
Credit Suisse AG |
credit-sussie.com/in /on/investment-banking |
|
CTBC Bank Co Ltd |
NA |
|
DBS Bank India Ltd |
dbs.com |
|
Deutsche Bank AG |
db.com |
|
Doha Bank |
dohabank.co.in |
|
Emirates NBD Bank (P.J.S.C) |
Emiratesnbd.co.in |
|
First Abu Dhabi Bank PJSC |
bankfab.com/en-in |
|
FirstRand Bank Ltd |
firstrand.co.za |
|
Industrial and Commercial Bank of China Ltd. (ICBC) |
icbcindia.com |
|
Industrial Bank Of Korea |
NA |
|
J P Morgan Chase Bank, N.A. |
jpmorgan.com |
|
JSC VTB Bank |
vtb.com |
|
KEB Hana Bank |
NA |
|
Kookmin Bank |
kbstar.com |
|
Krung Thai Bank Public Company LTD |
ktb.co.th/th/content/others/foreign-location-detail |
|
Mashreqbank psc |
mashreqbank.com |
|
Mizuho Bank Ltd. |
mizuhocbk.co.jp/english |
|
MUFG Bank Ltd |
mufg.jp/english |
|
National Australia Bank (NAB) |
nationalaustraliabank.com nabindia/en/home |
|
PT Bank Maybank Indonesia Tbk |
NA |
|
Qatar National Bank Q P S C. |
qnb.com |
|
Sberbank |
NA |
|
SBM Bank (India) Ltd. |
sbmgroup.mu |
|
Shinhan Bank |
|
|
Societe Generale |
societegenerale.in |
|
Sonali Bank Ltd. |
sbl.in |
|
Standard Chartered Bank |
standardchartered.com |
|
Sumitomo Mitsui Banking Corporation |
NA |
|
The Bank of Nova Scotia |
scotiabank.com |
|
The Hong Kong & Shanghai Banking Corporation Ltd. |
hsbc.co.in |
|
The Royal Bank of Scotland N V |
rbs.in |
|
United Overseas Bank Limited |
uobgroup.com |
|
Westpac Banking Corporation |
NA |
|
Woori Bank |
wooribank.com |
Regional Banks
Regional Rural Banks are government-owned scheduled commercial banks of India that operate at the regional level in different states of India.
-
These banks are under the ownership of the Ministry of Finance, Government of India.
-
They were created to serve rural areas with basic banking and financial services.
-
There are a total of 56 regional banks in India.
Co-operative Banks
Co-operative banks are financial entities established on a cooperative basis and belonging to their members.
-
This means that the customers of a cooperative bank are also its owners.
-
These banks provide a wide range of regular banking and financial services.
-
Also, these Cooperative Banks are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India and are governed by the Banking Regulation Act 1949, and Banking Laws Act 1955.
-
There are a total of 31 Cooperative Banks in India, which are individually under the Government to provide services to their employees.
Urban Co-operative Bank
The term Urban Co-operative Banks (UCBs), though not formally defined, refers to primary cooperative banks located in urban and semi-urban areas.
-
These banks, till 1996, were allowed to lend money only for non-agricultural purposes.
-
There are 1,531 urban cooperative banks (UCBs) and
The history of banking in India reflects the evolution of the country’s financial system, from ancient money lending practices to the establishment of modern banking institutions. The Indian banking sector has played a pivotal role in supporting economic development, facilitating trade, and promoting financial inclusion.
The journey of Indian banking began with traditional indigenous bankers and evolved through the founding of key institutions such as the Bank of Hindustan (1770), the Presidency Banks, and later the formation of the Imperial Bank of India in 1921, which eventually became the State Bank of India in 1955. Major milestones such as the nationalization of banks in 1969 and 1980, the establishment of Regional Rural Banks (RRBs), NABARD, and the liberalization of the banking sector in the 1990s shaped the modern banking landscape of India.
For aspirants preparing for Banking, SSC, UPSC, and other government examinations, understanding the history of banking in India is crucial for answering questions in the General Awareness, Banking Awareness, and Economy sections. This article provides a timeline of key events, major reforms, and institutions that have defined India’s banking sector.
rural cooperative banks, with the latter making up 65% of the total asset size of all cooperatives taken together.
State Co-operative Bank
-
The state cooperative bank is a federation of the central cooperative bank and acts as custodian of the cooperative banking structure in the State.
-
Its funds are obtained from the social capital, deposits, loans, and overdrafts of the Reserve Bank of India.
Top 10 Indian Banks - As per the largest Market Capitalisation
The top 10 Indian banks by market capitalization for 2024 are shown below. There are 21 private sector banks and 12 public sector banks in India. In addition, the Indian financial system is supported by 45 international banks operating in the private sector.
-
HDFC Bank
-
State Bank of India
-
ICICI Bank
-
Axis Bank
-
Kotak Mahindra Bank
-
IndusInd Bank
-
Yes Bank
-
Punjab National Bank
-
Bank of Baroda
-
Bank of India
|
Reasoning Free Study Materials PDF |
|||||
|
Order and Ranking |
|||||
|
|
|||||
FAQs
Q. Why is it important to study the history of banking in India for exams?
Questions on the history of banking regularly appear in Banking, SSC, UPSC, Railway, and other government exams, especially in General Awareness, Banking Awareness, and Economy sections. It helps candidates understand how India’s financial system evolved and its impact on the economy.
Q. When did modern banking begin in India?
Modern banking in India began with the Bank of Hindustan, established in 1770, followed by the Presidency Banks in the 19th century.
Q. What was the significance of bank nationalization?
The nationalization of 14 major banks in 1969 and 6 more in 1980 aimed to ensure that banking services reached rural and underserved areas, promoting financial inclusion and social development.
Q. Does the PDF cover key reforms and timelines?
Yes! The PDF provides a detailed timeline of key milestones, from early banks to reforms like nationalization, the setting up of RRBs, NABARD, and banking sector liberalization in the 1990s.
Q. Is this PDF useful for quick revision before exams?
Absolutely! The PDF is designed as a quick-reference tool, summarizing important dates, institutions, and reforms for easy last-minute revision.
Q. Is the PDF available in both English and Hindi?
Yes, the History of Banking in India PDF is provided in both English and Hindi to help candidates from different language backgrounds.
Q. Does the PDF include details about key banking institutions?
Yes! The PDF covers major institutions such as the State Bank of India (SBI), Reserve Bank of India (RBI), NABARD, RRBs, and others that played a critical role in India’s banking evolution.
Q. How can I memorize the key milestones of banking history effectively?
You can use timelines, charts, or flashcards (check the PDF for a timeline) and attempt quick quizzes to reinforce your learning.
Q. What was the role of the Imperial Bank of India in Indian banking history?
The Imperial Bank of India, formed in 1921 by merging the three Presidency Banks (Bombay, Calcutta, Madras), acted as a commercial bank and performed certain central banking functions before the establishment of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in 1935.
Q. When was the Reserve Bank of India established, and why is it important?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) was established in 1935 as the central bank of India. It regulates the country’s monetary policy, issues currency, and ensures financial stability.
|
Quantitative Aptitude Free Study Materials PDF |
|||||
|
|
|||||
General Awareness Smart Analysis (Smart Quiz 2.0)
- Get Weekly 4 set Test
- Each Set consist of 50 Questions
- Compare your progress with Test 1 & 2 & Test 3 & 4
- Deep Analysis in topic wise questions
Super Plan
- All Banking PDF Course 2026, 2025, 2024
- All Banking Video Course
- All Banking Mock Test Series
- All Banking Bundle PDF Courses
- All Banking Ebooks
- All Banking Interview Courses Not Included
Premium PDF Course
- Bundle PDF Course 2025
- Premium PDF Course 2024
- Prime PDF Course 2023







