-
Has a strong domestic as well as international presence.
-
Offers a wide range of retail and corporate banking services, including savings accounts, loans, and credit cards.
-
Operates an extensive network of over 9,693 branches and 10,033+ ATMs across India.
Check the Expected Questions from Indian Government Banks 2026
Punjab National Bank (PNB)
-
One of the oldest public sector banks, originally established in Lahore (now in Pakistan).
-
Specialises in retail banking, corporate banking, and wealth management services.
-
Has an extensive network of over 10,108 branches and 12,455 ATMs across India.
Indian Overseas Bank (IOB)
-
Established mainly to support international trade and overseas banking requirements.
-
Offers retail banking, international trade solutions, MSME lending, and corporate finance services.
-
Known for its strong global presence, along with a wide domestic network.
Canara Bank
-
Founded in 1906 and headquartered in Bangalore.
-
Focuses on MSME financing, agriculture, retail banking, and project finance.
-
Operates through a large network of more than 9,604 branches and 12,155 ATMs.
Check About Payment Banks of India 2026
Union Bank of India
-
Provides a wide range of financial services, including retail and corporate banking.
-
Actively involved in financial inclusion initiatives.
-
Has a strong nationwide presence with over 8,500 branches and 10,000+ ATMs.
Indian Bank
-
Established in 1907 and known for comprehensive retail and corporate banking solutions.
-
Offers products such as loans, savings accounts, credit cards, and digital banking services.
-
Operates through a network of over 5,847 branches and 4,937 ATMs across India.
UCO Bank
-
Founded in 1943 with a strong focus on rural development and financial inclusion.
-
Provides microfinance, retail banking, and corporate banking services.
-
Has over 4,000 branches and an international presence in Hong Kong and Singapore.
Check the Role and Functions of Banks in India
Bank of India (BOI)
-
Known for a wide range of banking products, including personal, corporate, and MSME banking.
-
Headquartered in Mumbai with more than 5,100 branches across the country.
-
Offers competitive loan schemes and advanced digital banking services.
Central Bank of India
-
Established in 1911 and known for its strong rural and semi-urban outreach.
-
Specialises in agricultural lending, MSME finance, and government-sponsored schemes.
-
Operates through an extensive network of over 4,500 branches nationwide.
List of Public Sector Banks with Headquarters 2026
List of 12 PSU Banks in India 2026 |
|||||
|
S.No |
Public Sector Banks |
Tagline |
Government |
Established |
Headquarters |
|
1 |
State Bank of India |
Pure Banking, Nothing Else |
57.59% |
1955 |
Mumbai, Maharashtra |
|
2 |
Punjab National Bank |
The Name You Can Bank Upon |
73% |
1894 |
New Delhi, Delhi |
|
3 |
Bank of Baroda |
India's International Bank |
63.97% |
1908 |
Vadodara, Gujarat |
|
4 |
Bank of India |
Relationship Beyond Banking |
73.38% |
1906 |
Mumbai, Maharashtra |
|
5 |
Bank of Maharashtra |
Ek Parivaar, Ek Bank (One Family One Bank) |
79.06% |
1935 |
Pune Maharashtra |
|
6 |
Union Bank of India |
Good People to Bank with |
74.76% |
1919 |
Mumbai, Maharashtra |
|
7 |
Canara Bank |
Together We Can |
62.93% |
1906 |
Bengaluru, Karnataka |
|
8 |
Central Bank of India |
Central to You Since 1911, Build a better life around us |
93.08% |
1911 |
Mumbai, Maharashtra |
|
9 |
Indian Bank |
Your Own Bank: Banking That's Twice As Good |
73.84% |
1907 |
Chennai, Tamil Nadu |
|
10 |
Indian Overseas Bank |
Good People To Grow With |
96.61% |
1937 |
Chennai, Tamil Nadu |
|
11 |
Punjab and Sind Bank |
Where Service is a Way of Life |
98.25% |
1908 |
New Delhi |
|
12 |
UCO Bank |
Honours your Trust |
90.95% |
1943 |
Kolkata, WB |
Largest Public Sector Banks After Merger
The largest government banks in India, as of 2026, after mergers, are tabulated below.
Largest Public Sector Banks After Merger |
|
|
Bank |
Rank |
|
State Bank of India |
1 |
|
Punjab National Bank |
2 |
|
Bank of Baroda |
3 |
|
Canara Bank |
4 |
|
Union Bank |
5 |
|
Bank of India |
6 |
|
Indian Bank |
7 |
|
Central Bank of India |
8 |
|
Indian Overseas Bank |
9 |
|
UCO Bank |
10 |
|
Bank of Maharashtra |
11 |
|
Punjab & Sind Bank |
12 |
Role of Government Banks in the Indian Economy
The major roles that government banks play in the Indian Economy are listed below.
-
Financial inclusion: Jan Dhan–led initiatives and digital reforms have transformed financial inclusion in India. By expanding access to banking services and strengthening social security for vulnerable groups, these measures have empowered millions and promoted a more inclusive society. Financial inclusion schemes ensure the availability of credit, insurance, pension coverage, and economic awareness among the weaker sections. Their impact is wide-ranging, with strong multiplier effects on the economy. The JAM (Jan Dhan–Aadhaar–Mobile) trinity has played a crucial role in integrating the unbanked into the formal financial system.
-
Credit to Agriculture and MSMEs: Public Sector Banks (PSBs) provide the majority of loans for agriculture, accounting for approximately 70-75% of all lending in this sector. According to the Reserve Bank of India’s rules, banks must allocate 18% of their net credit to agriculture. They support farmers through programs like Kisan Credit Cards, interest subsidies, and loans for farm infrastructure. PSBs are also essential for the growth of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs). They meet required lending goals, offer collateral-free loans through schemes like PMMY and CGTMSE, and provide working capital, digital services, and advice to help encourage entrepreneurship and job creation.
-
Government schemes implementation: To address rising stress in the banking system, the RBI initiated the Asset Quality Review (AQR) in 2015, leading to transparent recognition of NPAs, which peaked in 2018 and impacted bank finances. In response, the Government launched reforms such as Indradhanush, bank recapitalisation, IBC, EASE, governance reforms, and bank amalgamation under the 4R strategy. These measures significantly improved asset quality, capital adequacy, profitability, and overall resilience of banks, restoring lending capacity and financial stability.
Difference Between Government Banks and Private Banks in India
| Government Banks and Private Banks in India - Differences | ||
| S. No | Government Banks of India | Private Banks in India |
| 1 | Owned and controlled by the Government of India | Owned by private individuals or corporate entities |
| 2 | Through national-level exams conducted by IBPS, SBI, etc. | Direct recruitment by banks through interviews and assessments. |
| 3 | High job security with stable service conditions | Relatively lower job security, performance-driven |
| 4 | Focus on public welfare, rural banking, and priority sector lending | Emphasis on customer-centric services, innovation, and technology |
List of Indian Government Banks After Merger
The bank's mega-merger was announced by Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman in 2019. Bank mergers are conducted to reduce the operational costs of banks, enhance risk management, and improve professional standards. The bank mergers and acquisitions are provided here.
List of Government Banks After the Merger |
|
|
State Bank of India, State Bank of Bikaner And Jaipur, State Bank of Hyderabad, State Bank of Mysore, State Bank of Patiala, State Bank of Travancore, Bharatiya Mahila Bank |
1st largest Public Sector Bank |
|
Punjab National Bank, Oriental Bank of Commerce, and United Bank |
2nd largest Public Sector Bank |
|
Bank of Baroda, Dena Bank, and Vijaya Bank |
3rd largest Public Sector Bank |
|
Canara Bank and Syndicate Bank |
4th largest Public sector Bank |
|
Union Bank, Andhra Bank, and Corporation Bank |
5th largest Public Sector Bank |
|
Indian Bank and Allahabad Bank |
7th largest Public sector Bank |
Features of Government Banks In India 2026
-
Wide Range of Banking Services
Government banks offer multiple financial products such as savings accounts, fixed deposits, loans, credit cards, and insurance for both individuals and businesses. -
Smooth Financial Transactions
They provide facilities like foreign exchange, remittances, and money transfers, enabling customers to carry out domestic and international transactions easily. -
Safety of Deposits
As custodians of public funds, government banks ensure strong security and stability, giving depositors confidence that their money is safe. -
Strict Regulatory Oversight
These banks operate under the supervision of regulatory authorities like RBI and SEBI and follow stringent rules to maintain transparency and protect depositors’ interests. -
Strong Governance and Risk Control
Government banks follow robust corporate governance and risk management practices, remain accountable during economic challenges, and take decisions that safeguard both the institution and its customers.
Check the Development Banks In India
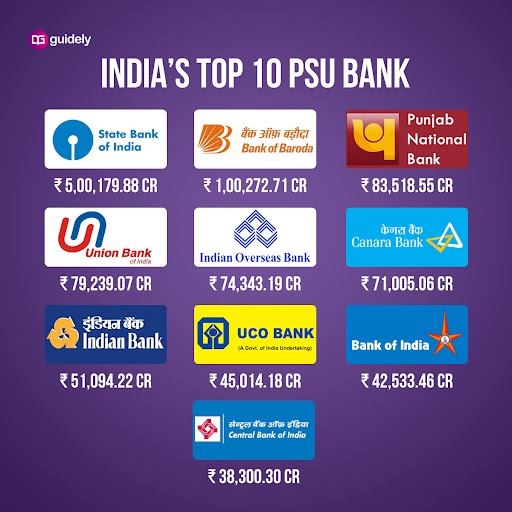
Assets Held By Top 10 Government Banks In India
The State Bank of India topped the list with a total of ₹ 7170899 crore (INR).